Refractive errors have in common that the sight is defective because of the lack of focus of the image on the retina. It is due to an anomaly in the form of the eyeball, of the crystalline lens or of the cornea.
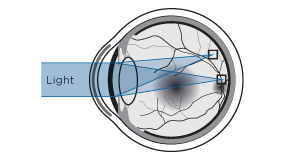
Normal eye
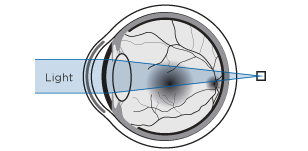
In the emmetropic or normal eye the light rays focus just on the retina, allowing the brain to perceive sharp images (emmetropia).
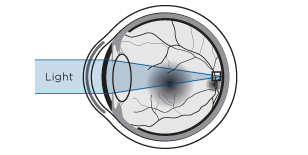
Myopia
When the eyeball is longer than normal, the light rays form the image in front of the retina, provoking a blurred sight of distant objects and a sharp sight of nearer objects.
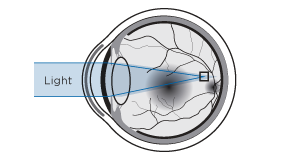
Hyperopia
When the eyeball is slightly shorter than normal, the light rays form the image beyond the retina, provoking a blurred sight of distant and near objects. Due to an extra readjustment made by the cilliary muscle, the young farsighted usually see distant objects correctly, although they also suffer a certain fatigue because of that effort.
Astigmatism
When the corneal curvature radiuses are not equal, the light rays do not focus on a single point, provoking a distortion of the image –which is usually well focused horizontally but not in the vertical direction– and a blurry sight of distant and near objects. This pathology can appear alone or together with myopia or Hyperopia.
Presbyopia
Because of the aging of the eye (between 40 and 50 years of age), the crystalline lens loses its flexibility, provoking incapability to focus, especially in the short distance.
Surgical treatments
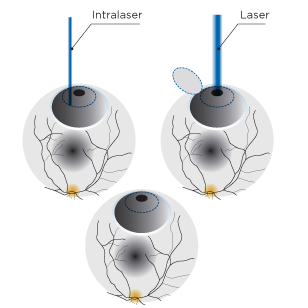
Excimer laser (Lasik)
It is a brief intervention where topical anesthesia (eyedrops) is used; it is an outpatient surgery and allows a quick recovery. The method consists in making a cut, flap or corneal hinge using a Intralase laser beam. Then the corneal area underneath is shaped with the laser and finally the flap is laid back and it adheres itself at the most in 24 hours. The following day of the intervention the patient can already make her or his everyday activities normally.
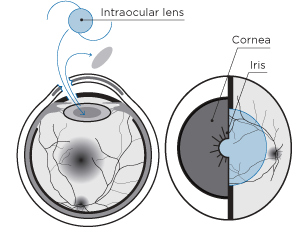
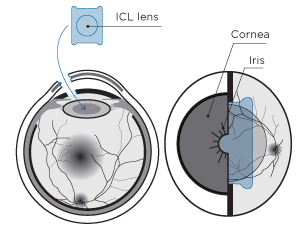
Intraocular contact Lens (ICL)
This involves the introduction of an intraocular lens with the necessary diopters inside the eye, in front of the crystalline lens.
This kind of surgery can be performed in patients with myopia, astigmatism or hyperopia.
Lensectomy with implant of intraocular lens
It is an intervention where the natural crystalline lens is replaced by an intraocular lens that can be monofocal or multifocal.
This kind of surgery is reserved for the cases where the lasik and the implant of ICL are contraindicated.